
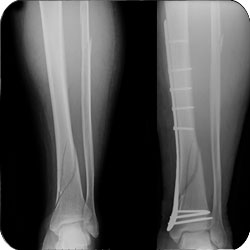
Unstable weber B fracture requires surgical fixation. Weber type B the distal fibula fracture is located at the same level of the syndesmosis. Injuries of this type could be treated conservatively if it is a stable injury (no deltoid ligament injury nor syndesmotic injury).This type of fracture is usually stable and can be treated conservatively. Weber type A the distal fibula fracture is below the level of the syndesmosis.This system categorizes ankle fractures based on distal fibula fracture line localization relative to the syndesmosis into three types: Trimalleolar ankle fracture the three ankle malleoli (medial, lateral, and posterior) are broken.Bimalleolar ankle fracture two malleoli are fractured, either the medial and lateral malleoli or less commonly the poster and lateral malleoli.
#DISTAL TIBIA FIBULA FRACTURE FULL#
Whenever the ring is broken, it happens in two places. Based on the evaluation of ankle fractures, a full assessment of the whole ankle ring is necessary to avoid missing any bony or ligamentous injury. Different systems have been developed to classify ankle fractures.Ĭlassifies ankle fractures depending on the anatomical location into The ankle joint bony and ligamentous structures from a complete ring. Open ankle fractures incidence is about 2% of all ankle fractures. About 20 % of ankle fractures are bimalleolar fractures, while trimalleolar fractures represent about 7% of all ankle fractures. Isolated uni malleolar fractures are the most common type accounting for 70% of the yearly incidence of all ankle fractures. The highest incidence in the female population is between 75 and 84 years old, compared to 15 to 24 years old for males. EpidemiologyĪbout 100 adults sustain ankle fractures every year. The degree of bony comminution and soft tissue damage is directly related to the energy of trauma. Ankle crush injury may be caused by a road traffic accident or crushing the ankle underneath a heavy object. Impact injuries may result from falling from a height with impaction of the distal tibia and fibula against the talus. Falling, tripping, or sports activities may cause twisting forces through the ankle. EtiologyĪnkle fractures can be caused by various modes of trauma, e.g., twisting, impact, and crush injuries. Branches from the peroneal, anterior, and posterior tibial arteries provide the arterial supply to the ankle joint. The ankle joint is innervated by articular branches from the tibial nerve, superficial and deep peroneal nerves.
The lateral ligament complex resists the ankle from over the inversion. The lateral ligaments complex consists of three ligaments originating from the lateral malleolus and attaches to the talus (anterior and posterior talofibular ligaments) and the calcaneus(calcaneofibular ligament). The deltoid ligament originates from the medial malleolus and attaches to the talus, navicular, and calcaneus bones and stabilizes the ankle joint against over eversion. The syndesmosis is formed by three main parts the interosseous tibiofibular ligament, the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, and the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. The ankle syndesmosis is a fibrous joint connecting the distal tibia and fibula. The ankle joint entires three malleoli the lateral malleolus (distal end of the fibula), medial malleolus (medial lower end of the tibia), and the posterior malleolus.Īnkle joint stability is provided by the ankle mortise articulation with the talus body, the ankle syndesmosis, the ligaments and muscles around the ankle joint. The distal tibia and fibula articular portions together form the ankle mortice, which contains the body of talus bone.
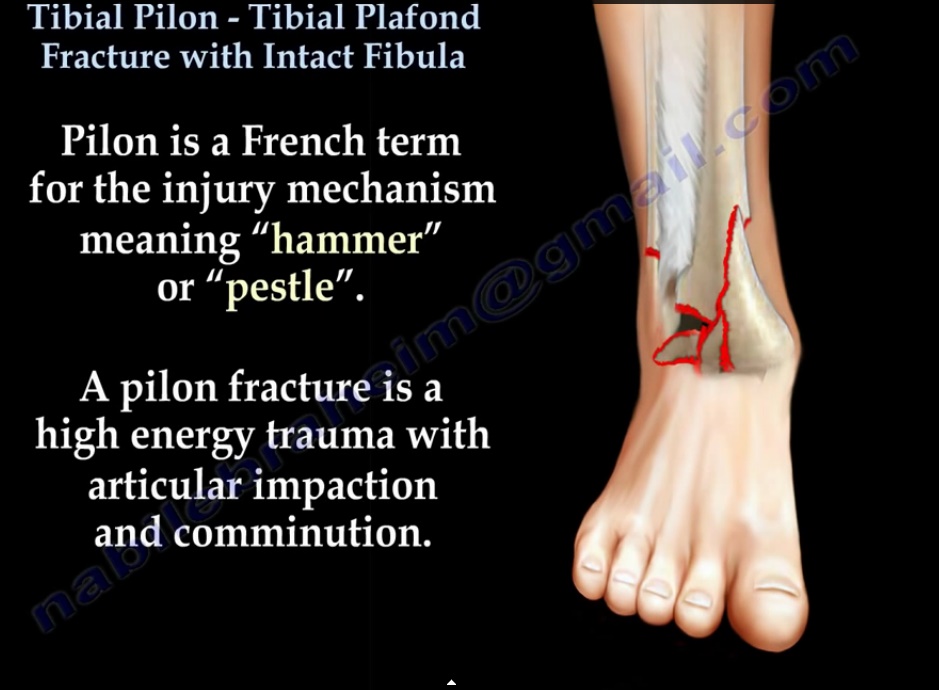
It is formed by the articulation between three bones distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus bone. The ankle joint is a hinge synovial joint that moves in one plane to produce dorsiflexion and plantar flexion. Treatment of these fractures aims to restore joint stability and alignment to reduce the risk of post-traumatic ankle arthritis.
#DISTAL TIBIA FIBULA FRACTURE HOW TO#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
